Are Plant-Based Proteins Sufficient for Bariatric Patients?
After bariatric surgeries such as sleeve gastrectomy, protein needs increase significantly to support tissue repair and prevent muscle loss. The typical recommendation is 60–80 grams of protein per day. While it’s possible to meet this requirement with plant-based sources alone, it requires careful planning and conscious choices. Since plant-based proteins generally have lower bioavailability compared to animal-based ones, combinations, supplementation, and cooking methods become crucial.
Lentils, Chickpeas, and Beans: When to Introduce Them?
Legumes are rich in both fiber and plant-based protein. However, due to potential digestive discomfort post-surgery, they are typically recommended starting from weeks 6–8. During the purée phase, softer options like hummus made from mashed chickpeas are more tolerable. To reduce gas and bloating:
- Soak overnight
- Discard the cooking water
- Add spices like cumin for better digestion
Tofu and Tempeh: Key Tips for Consumption
Soy-based products like tofu and tempeh are standout plant proteins due to their high protein content and ease of digestion.
- Tofu, especially soft or silken varieties, can be added to purées or soups.
- Tempeh, being fermented, supports gut health and can be included in soft sautéed dishes.
Cooking Tips:
- Steam to soften
- Prefer sautéing over grilling or baking
- Keep oil usage minimal
Balancing Plant Protein with Vitamin Supplements
Key nutrients to monitor on a plant-based diet include:
- Vitamin B12: Not found naturally in plant-based foods—supplementation is essential
- Iron: Non-heme iron from plants is less bioavailable; pair with vitamin C to boost absorption
- Zinc & Omega-3: Often lacking in vegetarian diets; consider supplements as needed
Working with a healthcare provider to create a personalized supplement plan is strongly recommended.
Is Vegan or Vegetarian Bariatric Nutrition Possible?
Absolutely, but strategic planning is key. Vegan and vegetarian bariatric patients should:
- Include a protein source at every meal
- Use food combinations (e.g., whole grains + legumes) for complete proteins
- Monitor potential deficiencies in B12, Vitamin D, iron, and other micronutrients
Partnering with a registered dietitian greatly increases success.
Gas-Friendly Plant-Based Alternatives
Gas and bloating are common post-sleeve gastrectomy. If legumes cause issues, consider:
- Instead of legumes: Try lentil- or quinoa-based soups, mashed tofu, or vegetable purées enriched with eggs
- Add probiotics: Opt for yogurt (or dairy-free alternatives), kefir, or probiotic supplements
- Start with small portions and gradually increase as tolerated
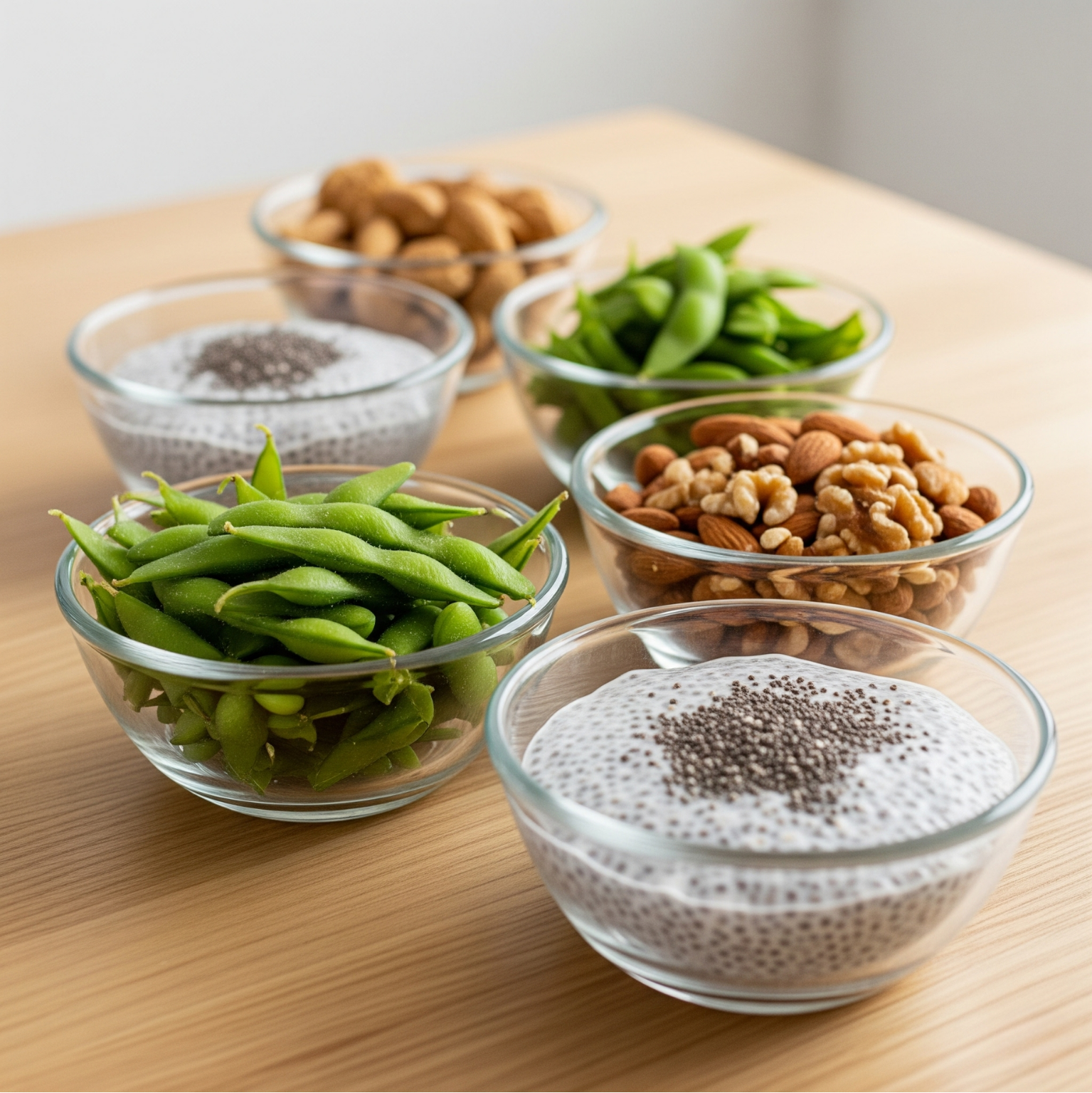
Protein Content of Grains and Nuts
While whole grains and nuts are valuable protein sources, portion control is crucial:
| Food | Protein per 100g |
| Quinoa | 14 g |
| Buckwheat | 13 g |
| Chia Seeds | 17 g |
| Walnuts | 15 g |
| Almonds | 21 g |
| Oats | 13 g |
Due to high fat content, limit nuts to about 1 tablespoon per serving.
Plant-Based Smoothie Ideas for Bariatric Diets
Smoothies are convenient and easy to digest. Here are protein-rich, plant-based ideas:
- Green Protein Smoothie
Spinach + 1 tbsp chia seeds + unsweetened almond milk + vegan protein powder - Creamy Tofu Smoothie
½ soft tofu + 1 banana + 1 tsp peanut butter + cinnamon - Oat-Based Protein Smoothie
Cooked oats + almond milk + frozen blueberries
Ensure your smoothie has a light consistency—avoid overly thick textures.
Cooking Methods That Improve Digestion
To make plant-based foods more digestible:
- Steaming: Gentle and ideal for retaining nutrients
- Boiling: Especially good for legumes and vegetables
- Blending: Use a blender during early stages to purée foods and ease digestion
Avoid frying or using heavy spices that may irritate the stomach.
How to Improve Plant Protein Absorption
- Pair with Vitamin C: E.g., lentil soup with lemon boosts iron absorption
- Fermented foods: Such as tempeh enhance digestion and nutrient uptake
- Smart combinations: Pair complementary proteins like quinoa + beans, or whole wheat + lentils
- Chew thoroughly and eat slowly to improve digestion
Conclusion
For post-bariatric individuals who avoid meat, plant-based protein sources can absolutely meet nutritional needs—if approached with care. From lentils to tofu, oats to nuts, a wide variety of options can form the basis of a healthy and sustainable diet. Whether you’re vegan or vegetarian, success in bariatric nutrition is entirely achievable with the right knowledge and support.