Bariatric surgery is a life-changing step in the fight against obesity. However, true success comes from preventing weight regain after surgery. The foundation of long-term weight maintenance in bariatric nutrition lies in finding the right balance between protein and fiber.
With a smaller stomach, every bite must be nutrient-dense — protein helps preserve muscle mass, while fiber promotes satiety and prevents hunger spikes.
The Vital Role of Protein and Fiber in Weight Maintenance
After bariatric surgery, these two macronutrients are the keys to lasting success. But why are they so important?

Protein: The Protector of Muscle Mass
During rapid weight loss, the body tends to lose not only fat but also muscle. Muscle loss causes the metabolism to slow down and makes weight gain easier in the future. Adequate protein intake prevents this.
- Daily Requirement: The daily protein requirement in the postoperative period is generally between 60–80 grams.
- Best Sources: Lean animal proteins such as eggs, skinless chicken and turkey breast, and fish have high biological value. Dairy products like yogurt, kefir, and cheese are also excellent options. For vegetarians, tofu, edamame, and lentils are top choices.
Fiber: The Key to Satiety and Digestive Health
Fiber-rich foods move slowly through the digestive tract, keeping your stomach full longer. This helps reduce snacking between meals and supports portion control.
Both Types Matter:
- Soluble fiber (found in oats and legumes) helps balance blood sugar.
- Insoluble fiber (found in whole grains and vegetables) supports bowel regularity and prevents constipation.
Best Sources: Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and zucchini; legumes such as chickpeas and lentils; and small portions of whole-grain products.
Practical Meal Planning: Balancing Protein and Fiber
Turning theory into practice is the key to sustainable weight maintenance after bariatric surgery. Here are some effective strategies:
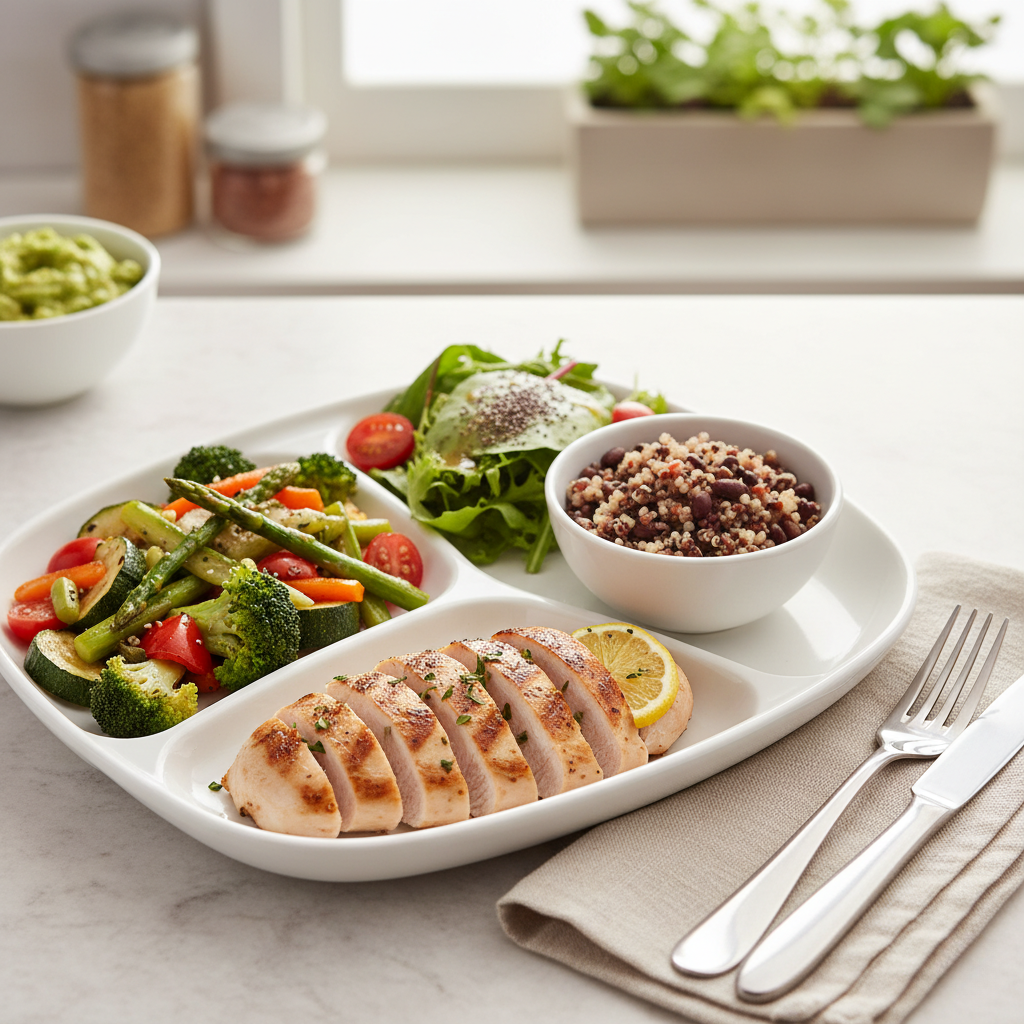
The Ideal Plate Model for Portion Control
Following the “plate method” makes balanced eating easier:
- Half of the plate (50%): Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, cucumber (Fiber)
- One quarter (25%): Lean protein such as grilled chicken, fish, or tofu (Protein)
- One quarter (25%): Complex carbohydrates like lentils, quinoa, or whole-grain bread (Fiber + Energy)
You can also explore our healthy and filling salad recipes for inspiration.
Smart Combinations for Balanced Blood Sugar
Consuming protein and fiber together slows down the absorption of carbohydrates and prevents blood sugar spikes — reducing hunger and sugar cravings.
Example Combo: Grilled salmon served with a green salad.
Snack Idea: A bowl of yogurt topped with one tablespoon of chia seeds and a few fresh berries.
Protein-Rich Snacks That Keep You Full
Snacks help prevent overeating by keeping you full until the next meal. Choose protein-based options instead of carb-heavy ones:
- A slice of cheese
- A handful of almonds (in moderation)
- A boiled egg
- Unsweetened, high-protein yogurt
Protein Supplements: When and How to Use Them
In the early post-op phase, reduced appetite and limited food intake can make it difficult to meet protein needs. Protein powders, shakes, or bars can be helpful — but use them wisely:
- Consult First: Always check with your doctor or dietitian before choosing a product.
- Check the Label: Avoid those with added sugar, artificial sweeteners, or unnecessary additives.
- Remember: Supplements should complement, not replace, real food sources of protein.
You can also check out our article on Protein Powders After Bariatric Surgery.
Conclusion: Long-Term Habits for Sustainable Success
Weight maintenance after bariatric surgery isn’t a short-term diet — it’s a lifelong lifestyle change.
By centering each meal around the protein–fiber balance, you’ll not only maintain your weight but also improve your overall health, boost your energy, and support digestive wellness.
Remember, your strongest ally on this journey is consistent, balanced, and sustainable eating habits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How much fiber should I eat per day after gastric sleeve surgery?
A: Aim for 25–30 grams of fiber per day. However, in the early post-op phase, your digestive system will be sensitive, so increase your fiber intake gradually under your dietitian’s guidance.
Q2: Do high-fiber foods cause gas or bloating? How can I prevent it?
A: Yes, they can. To reduce discomfort, introduce fiber-rich foods slowly, drink plenty of water throughout the day, and chew thoroughly.
Q3: Can I maintain my weight with just protein shakes?
A: No. Protein shakes are supplements, not replacements. To meet your body’s vitamin, mineral, and fiber needs, you must follow a balanced and varied diet.
Q4: Which carbohydrates can I eat during the weight maintenance phase?
A: Choose complex carbs such as quinoa, buckwheat, whole grains, and legumes in controlled portions, instead of simple carbs like white bread or sugary foods.
Q5: What should I do if I start regaining weight?
A: Don’t panic. Keep a food journal to track your intake, watch portion sizes, and increase your physical activity. Always consult your bariatric surgeon and dietitian for personalized support.