Why Do Sugar Cravings Occur in Bariatric Patients?
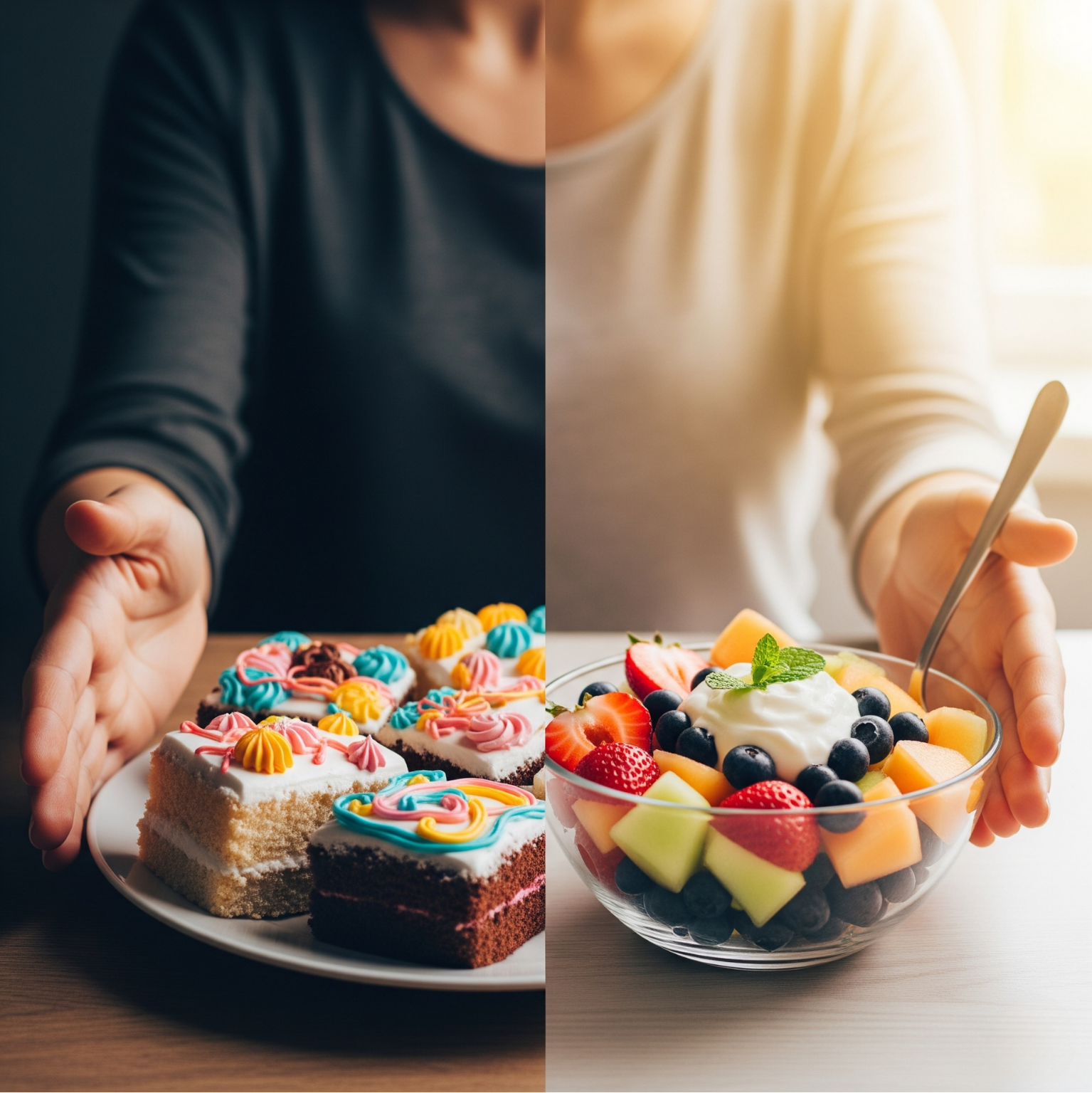
Sugar cravings are common among individuals who have undergone bariatric surgery. The main causes include hormonal changes, insufficient protein intake, episodes of low blood sugar, and emotional eating behaviors. Especially because the balance of appetite-regulating hormones like ghrelin and leptin shifts after surgery, cravings for sweets may increase.
Additionally, some individuals use sugar not just as an energy source but as an emotional reward, making sweet consumption almost inevitable. However, sugary foods can increase the risk of dumping syndrome and complicate weight control for bariatric patients.
Is It Possible to Make Refined Sugar-Free Desserts?
Yes, and they can be quite delicious! Desserts without refined sugar do not cause sudden blood sugar spikes, do not trigger excessive insulin release, and help keep you fuller for longer. Natural sweeteners such as banana, dates, pumpkin, and applesauce, when used with the right techniques, yield excellent results.
The key is to control portion sizes and increase the complex carbohydrate content to balance the glycemic load.
Low Glycemic Index Sweeteners
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Sweeteners with a low GI are ideal for bariatric patients because they digest slowly and steadily.
Use of Stevia, Erythritol, and Monk Fruit
- Stevia: A natural plant-based sweetener, calorie-free, and does not raise blood sugar.
- Erythritol: A sugar alcohol that does not stress the stomach and does not provoke an insulin response.
- Monk Fruit: A natural sweetener from China; zero-calorie and has antioxidant properties.
These sweeteners typically come in powder or liquid form and are suitable for baking. However, when using for the first time, start with small amounts to test stomach tolerance.
Easy No-Bake Dessert Examples
No-bake recipes are time-saving and easier to digest for bariatric individuals. Some examples include:
- Avocado chocolate pudding (sugar-free)
- Date oat balls
- Yogurt-based fruit mousse
- Coconut chia pudding
High fiber and protein content in these recipes provide a significant advantage in suppressing sugar cravings.
Protein-Rich Dessert Recipes for Fullness and Enjoyment
Protein delays gastric emptying, creating a longer-lasting feeling of fullness. Adding protein sources such as whey, yogurt, and egg whites to dessert recipes helps stabilize blood sugar and prevents muscle loss.
Popular recipe suggestions:
- Mini cheesecakes made with whey protein
- Cottage cheese oat bars
- Milk chia and protein powder dessert bowls
Protein desserts can also be used as light snacks replacing main meals.
Gluten-Free & Dairy-Free Dessert Options
Some individuals may have lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity, so dessert alternatives should be planned carefully.
- Plant-based milk recipes (almond, coconut milk)
- Legume flours (chickpea flour, lentil flour)
- Seeds (chia, flaxseed, hemp)
- Natural fiber sources (psyllium, coconut flour)
These recipes aid digestion and support gut health.
Practical Snack Alternatives Instead of Desserts
It is not always possible to prepare desserts. Practical, ready-to-eat, and portable alternatives can be lifesavers:
- Fresh fruit and walnut combinations
- Stuffed dates (with almonds or hazelnuts)
- Yogurt with cinnamon and chia mix
- Dark chocolate (minimum 85% cocoa content)
These snacks are low glycemic and provide quick satiety.
How to Balance Sweet Consumption with Portion Control?
Portion size is one of the most critical factors in sweet consumption. Since bariatric patients have a smaller stomach volume, consuming large amounts of sweets can cause nausea, bloating, or dumping syndrome.
Tips for portion control:
- Serve desserts in small containers
- Consume as snacks, not with main meals
- Balance sweets with protein and fiber content
- Weigh portions if necessary to keep control
How to Overcome Sweet Addiction?
Suppressing sweet cravings is not just a matter of willpower but requires managing biological and psychological processes. The following steps can help reduce addictive sweet consumption:
- Balance carbohydrate intake: Adequate complex carbs throughout the day prevent sudden cravings.
- Increase protein intake: Protein deficiency may trigger sweet cravings.
- Recognize emotional triggers: Food diaries can help identify these.
- Find alternative pleasure sources: Activities like exercise, music, and walking reduce the need for sweets.
- Practice mindful eating: Being fully aware of each bite increases control.
Conclusion: Staying Healthy Without Giving Up Sweets
Sugar cravings can be challenging for bariatric individuals, but with the right techniques and ingredients, these desires can be satisfied with healthy alternatives. Refined sugar-free, low glycemic index, and protein-rich recipes provide satiety while appealing to the palate.
Exploring sweet alternatives in bariatric nutrition supports not only physical but also psychological balance. Remember, the goal is not to give up sweets but to choose the right ones.